Rehabilitation is an important factor in enabling the body to restore function after an injury or illness. The aim is to help a patient achieve independence and get back to their original abilities as best they can. Brain injuries are one area in which rehabilitation is vital for assisting with this process.
While some brain injuries are unavoidable and are a result of illnesses such as brain tumours or strokes, they’re also commonly caused by trauma, including sports injuries, car accidents and falls. In some cases, a victim might be able to make a brain injury claim if the trauma was a result of someone else’s actions.
This type of injury can result in a variety of complications. These include blood clots, bleeding and fluid build-up.
Brain injuries are common, with statistics showing that, in the UK, someone is admitted to hospital every 30 seconds after suffering a brain injury. Patients can suffer both short and long-term problems following a brain injury, including:
Although the brain is unable to regenerate the damaged cells, which are often responsible for issues post-injury, it does have a unique ability to create new neural pathways to help the patient regain functionality. This impressive process is referred to as neuroplasticity.
These pathways are also created when we learn new skills and information, which is why millions of these connections are formed during the first three years of a child’s life.
The incredible fact about neuroplasticity is that this process can happen at any age, making it a key component when it comes to rehabilitation after a brain injury.
Rehabilitation is an important catalyst for helping the brain create new neural pathways. Rehabilitation programmes should be a priority in the care plan of a patient. They should also be tailored to the individual needs and specific brain injury to help the patient get the most out of post-injury care and therapy.
So, what does rehabilitation involve? Although specifics can vary across individuals, it often centres around:
The exact nature of rehabilitation depends on the severity of the damage. Often, the aim of these therapies is to help the brain re-learn tasks and skills, including movement and language, through frequent repetition.
As well as helping patients regain mobility and functionality, rehabilitation after a brain injury can assist with adapting to the home or social aspects of life. It can also help patients come to terms with their injury from a psychological standpoint.
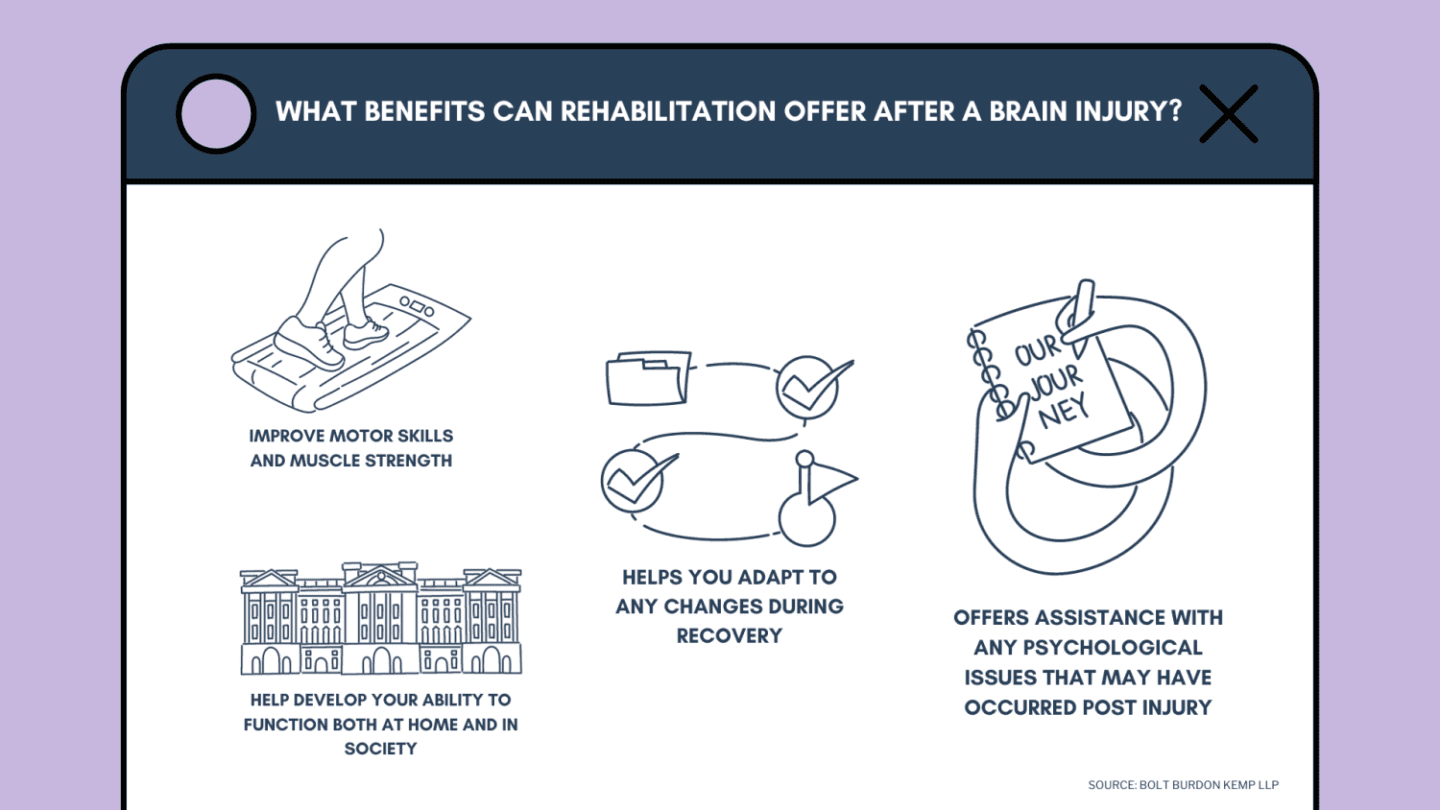
It’s important to recognise that each brain injury is different and, therefore, rehabilitation won’t look the same for every patient. Some individuals will benefit from a period of inpatient rehabilitation, especially if the injury is severe and they’re unable to return home for an extended amount of time.
Others will take part in outpatient or home-based rehabilitation programmes to help them adjust to independent living.
The length of time that a patient spends in rehabilitation can vary, depending on their progress and response to therapy. Some patients require ongoing care for months or years, while others make a quicker recovery.
Rehabilitation can also help provide support for loved ones. Family and friends have an important role to play in helping a patient return to previous mobility and function. Therapists, therefore, can help advise on the best ways to assist with this going forward.
Whatever the nature of a brain injury, it’s crucial not to underestimate the importance of a thorough rehabilitation programme. The brain itself is an astounding organ, which clearly has the ability to overcome even severe damage to its cells, even more so when assisted by tailored therapy.
This is a collaborative post.